本系列产品之前的Selenium该文让您了解了Selenium试验的基本原理。然而,在这首诗中,我将沙莱县如何采用Selenium架构来强化您的标识符内部结构,这将使您更接近成为Selenium证书的专精人员。
什么是Selenium架构?
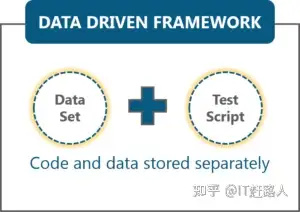
Selenium架构是一种标识符内部结构,用于精简标识符保护,提升标识符的时效性。架构涉及将整座标识符还原成更小的标识符短片,以试验某一的机能。 标识符的内部结构使得“统计数据集”与将试验web插件的机能的前述“单元试验”合二为一。它的内部结构也能是这样的:须要继续执行的单元试验能从内部插件(如.csv)初始化(初始化)。
统计数据驱动力架构URL驱动力架构混和架构为什么须要Selenium架构?
假如没有最合适的架构,将只有一个单元试验,它将包涵整座试验机能。可悲的是,这个单个的单元试验有能力上升到一千万行标识符。因而,很明显,如此巨大的单元试验将极难阅读。即使您接著想修正任何人机能,您也会极难修正标识符。 由于实现了一个架构,将产生更小但数个标识符短片,有各种益处。
Selenium架构带来的益处
减少标识符宠信提升了标识符时效性更高的便携性减少JAVA保护统计数据驱动力架构
Selenium中的统计数据驱动力架构是将“统计数据集”与前述的“单元试验”(标识符)分立的技术。该架构完全倚赖输出的试验统计数据。试验统计数据来自内部源,如EXCEL文件格式、.CSV文件格式或任何统计资料库。
因为单元试验与统计数据集为合二为一的,所以他们能随心所欲地修正某一机能的单元试验,而无须对您的标识符进行小规模更动。比如,假如您想修正登入机能的标识符,所以您能间接修正,而无须同时修正同一个标识符中的任何人其他倚赖部分。 除此以外,您还能随心所欲控制须要试验的统计信息量。 通过向excel文件格式(或其它源)加进更多帐号和公钥表头,您能随心所欲地减少试验模块的数量。 比如,假如我必须检查和页面的登入,所以我能将用户名和公钥凭证集留存在Excel文件格式中,并将凭证传达给标识符,以期在原则上的Java类文件格式中对应用程序继续执行智能化。
将Apache POI与Selenium WebDriver相互配合采用
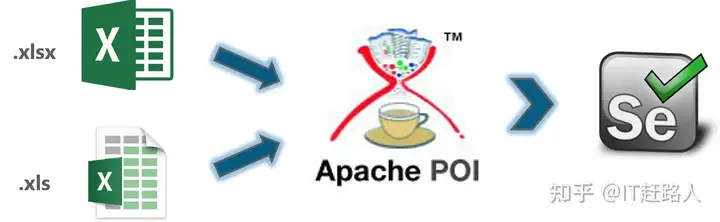
WebDriver不间接支持加载Excel文件格式。因而,他们采用Apache POI来读/写任何人Microsoft office文件格式。您能从这里浏览Apache POI(几组JAR文件格式)。根据您的需求浏览zip文件格式或tar文件格式,并将它们与Selenium JAR集放在一起。
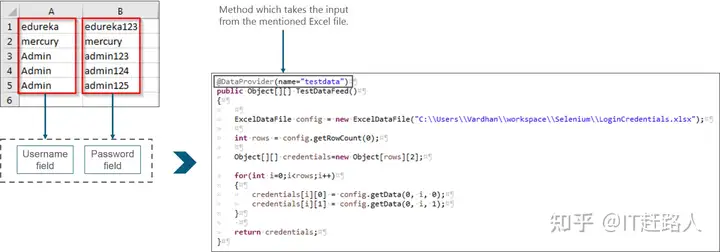
主标识符和统计数据集之间的协调将由testng统计数据提供程序负责,它是ApachePOI JAR文件格式的一部分。出于演示目的,我创建了一个名为“LoginCredentials”的Excel文件格式,其中的帐号和公钥存储在不同的列中。
请看下面的标识符以理解单元试验。这是一个简单的标识符,用于试验机票预订插件的登入机能。
package DataDriven;
import org.openqa.selenium.By;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeDriver;
import org.testng.Assert;
import org.testng.annotations.AfterMethod;
import org.testng.annotations.DataProvider;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class DDTExcel
{
ChromeDriver driver;
@Test(dataProvider=”testdata”)
public void DemoProject(String username, String password) throws InterruptedException
{
System.setProperty(“webdriver.chrome.driver”, “C:UsersVardhanDownloadschromedriver.exe”);
driver = new ChromeDriver();
driver.get(“http://newtours.demoaut.com/”);
driver.findElement(By.name(“userName”)).sendKeys(username);
driver.findElement(By.name(“password”)).sendKeys(password);
driver.findElement(By.name(“login”)).click();
Thread.sleep(5000);
Assert.assertTrue(driver.getTitle().matches(“Find a Flight: Mercury Tours:”), “Invalid credentials”);
System.out.println(“Login successful”);
}
@AfterMethod
void ProgramTermination()
{
driver.quit();
}
@DataProvider(name=”testdata”)
public Object[][] TestDataFeed()
{
ReadExcelFile config = new ReadExcelFile(“C:UsersVardhanworkspaceSeleniumLoginCredentials.xlsx”);
int rows = config.getRowCount(0);
Object[][] credentials = new Object[rows][2];
for(int i=0;i<rows;i++)
{
credentials[i][0] = config.getData(0, i, 0);
credentials[i][1] = config.getData(0, i, 1);
}
return credentials;
}
}
假如您从上面注意到,他们有一个名为“TestDataFeed()”的方法。在此方法中,我创建了另一个名为“ReadExcelFile”的类的对象实例。在实例化该对象时,我提供了包涵统计数据的myexcel文件格式的路径。我进一步定义了一个for循环来从excel工作簿中检索文本。但是,为了从给定的页码、列号和行号加载统计数据,须要初始化“ReadExcelFile”类。我的“ReadExcelFile”标识符如下。
package DataDriven;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFSheet;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook;
public class ReadExcelFile
{
XSSFWorkbook wb;
XSSFSheet sheet;
public ReadExcelFile(String excelPath)
{
try
{
File src = new File(excelPath);
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(src);
wb = new XSSFWorkbook(fis);
}
catch(Exception e)
{
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
public String getData(int sheetnumber, int row, int column)
{
sheet = wb.getSheetAt(sheetnumber);
String data = sheet.getRow(row).getCell(column).getStringCellValue();
return data;
}
public int getRowCount(int sheetIndex)
{
int row = wb.getSheetAt(sheetIndex).getLastRowNum();
row = row + 1;
return row;
}
}
首先注意我导入的库。我已经导入了Apache POI XSSF_LIBRARY,它们用于加载/写入统计数据到Excel文件格式。在这里,我创建了一个构造函数(相同方法的对象)来传达值:Sheetnumber、行号和列号。为了更好地理解这个架构,我请求您浏览一下下面的视频,我在视频中以内部结构化的方式对此进行了解释。
URL驱动力架构
URL驱动力架构是一种技术,其中要继续执行的所有操作和指令都与前述单元试验合二为一编写。 它与统计数据驱动力架构的相似之处在于,要继续执行的操作再次存储在内部文件格式(如Excel表格)中。
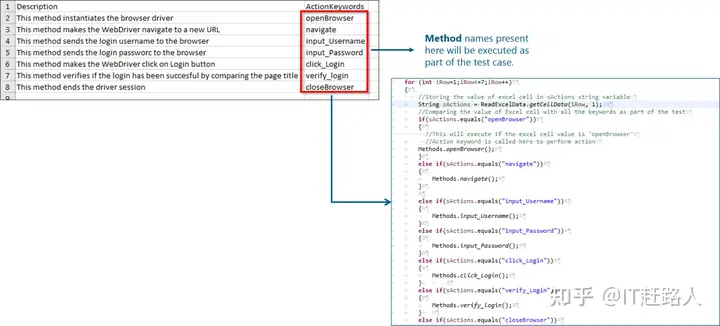
我所讨论的操作只不过是须要作为单元试验的一部分继续执行的方法。URL驱动力架构的益处是您能随心所欲控制要试验的机能。您能在Excel文件格式中指定试验应用程序机能的方法。因而,将只试验Excel中指定的那些方法名称。比如,为了登入到Web插件,他们能在主单元试验中编写多种方法,每个单元试验都将试验某些机能。为了实例化应用程序驱动力程序,能有一种方法,用于找到帐号和口令表头,能有方法,能有用于导航到页面的方法,能有另一种方法等等。
请看下面的标识符,以了解架构的外观。假如您不理解,下面标识符中注释掉的这些行能作为解释。
package KeywordDriven;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeDriver;
import org.testng.Assert;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import org.openqa.selenium.By;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
public class Actions
{
public static WebDriver driver;
public static void openBrowser()
{
System.setProperty(“webdriver.chrome.driver”, “C:UsersVardhanDownloadschromedriver.exe”);
driver=new ChromeDriver();
}
public static void navigate()
{
driver.manage().timeouts().implicitlyWait(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
driver.get(“http://newtours.demoaut.com”);
}
public static void input_Username()
{
driver.findElement(By.name(“userName”)).sendKeys(“mercury”);
}
public static void input_Password()
{
driver.findElement(By.name(“password”)).sendKeys(“mercury”);
}
public static void click_Login()
{
driver.findElement(By.name(“login”)).click();
}
@Test
public static void verify_login()
{
String pageTitle = driver.getTitle();
Assert.assertEquals(pageTitle, “Find a Flight: Mercury Tours:”);
}
public static void closeBrowser()
{
driver.quit();
}
}
如您所见,须要试验的不同机能存在于等待初始化的不同方法中。现在,基于Excel文件格式中存在的方法名称,这些方法将从另一个类初始化。类似地,为了加载EXCEL文件格式并返回结果,我编写了另一个类。它们都显示在下面。初始化这些方法的类文件格式如下所示。
package KeywordDriven;
public class DriverScript
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
//Declaring the path of the Excel file with the name of the Excel file
String sPath = “C:UsersVardhanworkspaceSelenium Frameworks DemodataEngine.xlsx”;
//Here we are passing the Excel path and SheetName as arguments to connect with Excel file
ReadExcelData.setExcelFile(sPath, “Sheet1”);
//Hard coded values are used for Excel row & columns for now
//Hard coded values are used for Excel row & columns for now
//In later chapters we will replace these hard coded values with varibales //This is the loop for reading the values of the column 3 (Action Keyword) row by row
for (int iRow=1;iRow<=7;iRow++)
{
String sActions = ReadExcelData.getCellData(iRow, 1);
//Comparing the value of Excel cell with all the keywords in the “Actions” class
if(sActions.equals(“openBrowser”))
{
//This will execute if the excel cell value is openBrowser
//Action Keyword is called here to perform action
Actions.openBrowser();
}
else if(sActions.equals(“navigate”))
{
Actions.navigate();
}
else if(sActions.equals(“input_Username”))
{
Actions.input_Username();
}
else if(sActions.equals(“input_Password”))
{
Actions.input_Password();
}
else if(sActions.equals(“click_Login”))
{
Actions.click_Login();
}
else if(sActions.equals(“verify_Login”))
{
Actions.verify_login();
}
else if(sActions.equals(“closeBrowser”))
{
Actions.closeBrowser();
}
}
}
}
加载Excel值的类文件格式如下所示。
package KeywordDriven;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFSheet;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFCell;
public class ReadExcelData
{
private static XSSFSheet ExcelWSheet;
private static XSSFWorkbook ExcelWBook;
private static XSSFCell Cell;
//This method is to set the File path and to open the Excel file
//Pass Excel Path and SheetName as Arguments to this method
public static void setExcelFile(String Path,String SheetName) throws Exception
{
FileInputStream ExcelFile = new FileInputStream(Path);
ExcelWBook = new XSSFWorkbook(ExcelFile);
ExcelWSheet = ExcelWBook.getSheet(SheetName);
}
//This method is to read the test data from the Excel cell
//In this we are passing parameters/arguments as Row Num and Col Num
public static String getCellData(int RowNum, int ColNum) throws Exception
{
Cell = ExcelWSheet.getRow(RowNum).getCell(ColNum);
String CellData = Cell.getStringCellValue();
return CellData;
}
}
混和架构
混和架构是一种能充分利用DataDriven和URL驱动力的Selenium架构的技术。采用本该文中显示的示例,他们能通过将要继续执行的方法存储在Excel文件格式中(URL驱动力方法)并将这些方法名称传达给Java反射类(统计数据驱动力方法)来构建混和架构,而不是在“DriverScript”类中创建ANIF/ELSE循环。 看看下面标识符短片中修正后的“DriverScript”类。 这里,不采用数个if/Else循环,而是采用统计数据驱动力的方法从Excel文件格式中加载方法名称。
package HybridFramework;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class DriverScriptJava
{
//This is a class object, declared as public static
//So that it can be used outside the scope of main[] method
public static Actions actionKeywords;
public static String sActions;
//This is reflection class object, declared as public static
//So that it can be used outside the scope of main[] method
public static Method method[];
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
//Declaring the path of the Excel file with the name of the Excel file
String sPath = “C:UsersVardhanworkspaceSelenium Frameworks DemodataEngine.xlsx”;
//Here we are passing the Excel path and SheetName to connect with the Excel file
//This method was created previously
ReadExcelData.setExcelFile(sPath, “Sheet1”);
//Hard coded values are used for Excel row & columns for now
//Later on, we will use these hard coded value much more efficiently
//This is the loop for reading the values of the column (Action Keyword) row by row
//It means this loop will execute all the steps mentioned for the test case in Test Steps sheet
for (int iRow=1;iRow<=7;iRow++)
{
sActions = ReadExcelData.getCellData(iRow, 1);
//A new separate method is created with the name execute_Actions
//You will find this method below of the this test
//So this statement is doing nothing but calling that piece of code to execute
execute_Actions();
}
}
//This method contains the code to perform some action
//As it is completely different set of logic, which revolves around the action only, it makes sense to keep it separate from the main driver script
//This is to execute test step (Action)
private static void execute_Actions() throws Exception
{
//Here we are instantiating a new object of class Actions
actionKeywords = new Actions();
//This will load all the methods of the class Actions in it.
//It will be like array of method, use the break point here and do the watch
method = actionKeywords.getClass().getMethods();
//This is a loop which will run for the number of actions in the Action Keyword class
//method variable contain all the method and method.length returns the total number of methods
for(int i = 0;i<method.length;i++)
{
//This is now comparing the method name with the ActionKeyword value received from the excel
if(method[i].getName().equals(sActions))
{ //In case of match found, it will execute the matched method
method[i].invoke(actionKeywords);
//Once any method is executed, this break statement will take the flow outside of for loop
break;
}
}
}
}