Vuex
甚么是Vuex?
非官方讲法:Vuex 是两个专为 Vue.js应用领域软件开发的状况区域化。它选用封闭式repeats应用领域的大部份模块的状况,并以适当的准则确保状况以一类可预估的形式发生改变。
对个人认知:Vuex是用以管理工作模块间通讯的两个应用领域程序
为甚么要用Vuex?
他们晓得模块间是分立的,模块间想同时实现通讯,我现阶段晓得的就多于props快捷键,但这也仅指父模块美树模块间的通讯。假如兄妹模块间想实现通讯呢?嗯..,形式假如有。撇开是不是同时实现的难题,换言之呵呵,当作中项目投资时,直面一堆模块间的通讯,除了一堆的形式论标识符,会不能很感到恐惧??那为何不把模块间共享资源的统计数据给“拎”出,在很大的准则下管理那些统计数据呢? 这是Vuex的基本上价值观了。
Vuex有甚么优点?
是不是采用Vuex?
导入Vuex.js文件
建立示例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang=”en”>
<head>
<meta charset=”UTF-8″>
<meta name=”viewport” content=”width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0″>
<meta http-equiv=”X-UA-Compatible” content=”ie=edge”>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<script src=”./js/vuex.js”></script>
<script src=”./js/vue2.0.js”></script>
<body>
<div id=”app”>
</div>
</body>
<script>
Vue.use(Vuex);//在建立Vue示例以后
var myStore = new Vuex.Store({
state:{
//放置模块间共享资源的统计数据
name:”jjk”
},
mutations:{
//隐式的更动state里的统计数据
});
new Vue({
el:”#app”,
data:{
name:”dk”
},
store:myStore,
mounted:function(){
console.log(this)//控制台
}
})
</script>
</html>
先解释上面标识符的意思:
new Vuex.Store({}) 表示建立两个Vuex示例,通常情况下,他需要注入到Vue示例里. Store是Vuex的一个核心形式,字面上认知为“仓库”的意思。Vuex Store是响应式的,当Vue模块从store中读取状况(state快捷键)时,若store中的状况发生更新时,他会及时的响应给其他的模块(类似双向统计数据绑定) 而且不能直接改变store的状况,改变状况的唯一形式是,隐式地提交更动(mutations快捷键)
他有4个核心快捷键:state mutations getters actions (下文会仔细分析)
这是上面标识符:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang=”en”>
<head>
<meta charset=”UTF-8″>
<meta name=”viewport” content=”width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0″>
<meta http-equiv=”X-UA-Compatible” content=”ie=edge”>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<script src=”./js/vuex.js”></script>
<script src=”./js/vue2.0.js”></script>
<body>
<div id=”app”>
<hello></hello>
</div>
</body>
<script>
Vue.use(Vuex);
var myStore = new Vuex.Store({
state:{
//放置模块间共享资源的统计数据
name:”jjk”
},
mutations:{
//隐式的更动state里的统计数据
},
getters:{
//过滤state统计数据
},
actions:{
//
}
});
Vue.component(hello,{
template:”<p>{{name}}</p>”,
computed: {
name:function(){
return this.$store.state.name
}
},
mounted:function(){
console.log(this)
}
})
new Vue({
el:”#app”,
data:{
name:”dk”
},
store:myStore,
mounted:function(){
console.log(this)
}
})
</script>
</html>
state:用以放置模块间共享资源的统计数据。他跟模块的data快捷键类似,只不过data快捷键是用以放置模块的私有统计数据。
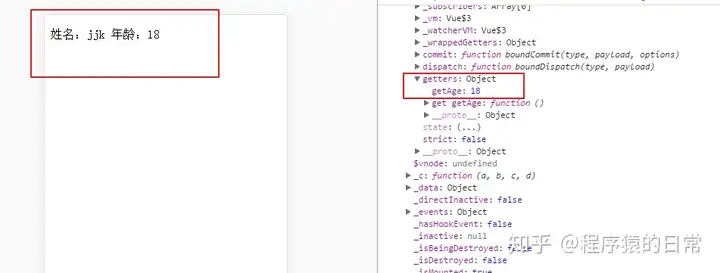
getters:有时候,他们需要对state的统计数据进行筛选,过滤。那些操作都是在模块的计算属性进行的。假如多个模块需要用到筛选后的统计数据,那他们就必须到处重复写该计算属性函数;或者将其提取到两个公共的工具函数中,并将公共函数多处导入 – 两者都不太理想。假如把统计数据筛选完在传到计滤的统计数据呢? 过滤的统计数据会放置到$store.getters对象中。具体看两个例子:<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang=”en”>
<head>
<meta charset=”UTF-8″>
<meta name=”viewport” content=”width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0″>
<meta http-equiv=”X-UA-Compatible” content=”ie=edge”>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<script src=”./js/vuex.js”></script>
<script src=”./js/vue2.0.js”></script>
<body>
<div id=”app”>
<hello></hello>
</div>
</body>
<script>
Vue.use(Vuex);
var myStore = new Vuex.Store({
state:{
//放置模块间共享资源的统计数据
name:”jjk”,
age:18
},
mutations:{
//隐式的更改state里的统计数据
},
getters:{
getAge:function(state){
return state.age;
}
},
actions:{
//
}
});
Vue.component(hello,{
template:”<p>姓名:{{name}} 年龄:{{age}}</p>”,
computed: {
name:function(){
return this.$store.state.name
},
age:function(){
return this.$store.getters.getAge
}
},
mounted:function(){
console.log(this)
}
})
new Vue({
el:”#app”,
data:{
name:”dk”
},
store:myStore,
mounted:function(){
console.log(this)
}
})
</script>
</html>
式是通过 提交(commit) 两个 mutation。 mutations下的函数接收state作为参数,接收两个叫做payload(载荷)的东东作为第二个参数,这个东东是用以记录开发者采用该函数的一些信息,比如说提交了甚么,提交的东西是用以干甚么的,包含多个字段,所以载荷一般是对象(其实这个东西跟git的commit很类似)除了一点需要注意:mutations形式必须是同步形式!
具体看示例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang=”en”>
<head>
<meta charset=”UTF-8″>
<meta name=”viewport” content=”width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0″>
<meta http-equiv=”X-UA-Compatible” content=”ie=edge”>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<script src=”./js/vuex.js”></script>
<script src=”./js/vue2.0.js”></script>
<body>
<div id=”app”>
<hello></hello>
</div>
</body>
<script>
Vue.use(Vuex);
var myStore = new Vuex.Store({
state:{
//放置模块间共享资源的统计数据
name:”jjk”,
age:18,
num:1
},
mutations:{
//隐式的更动state里的统计数据
change:function(state,a){
// state.num++;
console.log(state.num += a);
}
},
getters:{
getAge:function(state){
return state.age;
}
},
actions:{
//
}
});
Vue.component(hello,{
template:”<p @click=changeNum>姓名:{{name}} 年龄:{{age}} 次数:{{num}}</p>”,
computed: {
name:function(){
return this.$store.state.name
},
age:function(){
return this.$store.getters.getAge
},
num:function(){
return this.$store.state.num
}
},
mounted:function(){
console.log(this)
},
methods: {
changeNum: function(){
//在模块里提交
// this.num++;
this.$store.commit(change,10)
}
},
data:function(){
return {
// num:5
}
}
})
new Vue({
el:”#app”,
data:{
name:”dk”
},
store:myStore,
mounted:function(){
console.log(this)
}
})
</script>
</html>
相信很多人在刚接触前端或者中期时候总会遇到一些难题及瓶颈期,如学了一段时间没有方向感或者坚持不下去两对个人学习枯燥乏味有难题也不晓得是不是解决,对此我整理了一些资料 喜欢我的文章想与更多资深大牛一起讨论和学习的话 欢迎加入我的学习交流群